
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center of Material Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Photonics Laboratory, Munich University of Applied Sciences, Munich 80335, Germany
3 Institute for Measurement and Sensor Technology, Technical University of Munich, Munich 80333, Germany
4 College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
In the aerospace field, for aerospace engines and other high-end manufacturing equipment working in extreme environments, like ultrahigh temperatures, high pressure, and high-speed airflow, in situ temperature measurement is of great importance for improving the structure design and achieving the health monitoring and the fault diagnosis of critical parts. Optical fiber sensors have the advantages of small size, easy design, corrosion resistance, anti-electromagnetic interference, and the ability to achieve distributed or quasi-distributed sensing and have broad application prospects for temperature sensing in extreme environments. In this review, first, we introduce the current research status of fiber Bragg grating-type and Fabry–Perot interferometer-type high-temperature sensors. Then we review the optical fiber high-temperature sensor encapsulation techniques, including tubular encapsulation, substrate encapsulation, and metal-embedded encapsulation, and discuss the extreme environmental adaptability of different encapsulation structures. Finally, the critical technological issues that need to be solved for the application of optical fiber sensors in extreme environments are discussed.
optical fiber sensors high-temperature sensing encapsulation technique extreme environments Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(9): 090007

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Meteorology and Oceanology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Department of Physics, School of Science, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
We modify the pulse-reference-based compensation technique and propose a low-noise and highly stable optical fiber temperature sensor based on a zinc telluride film-coated fiber tip. The system noise is measured to be 0.0005 dB, which makes it possible for the detection of the minor reflectivity change of the film at different temperatures. The temperature sensitivity is 0.0034 dB/°C, so the resolution can achieve 0.2°C. The maximum difference of the temperature output values of the sensor at 20°C at different points in time is 0.39°C. The low cost, ultra-small size, high stability, and good repeatability of the sensor make it a promising temperature sensing device for practical application.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(7): 070603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Meteorology and Oceanology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 The Medical Engineering & Maintenance Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
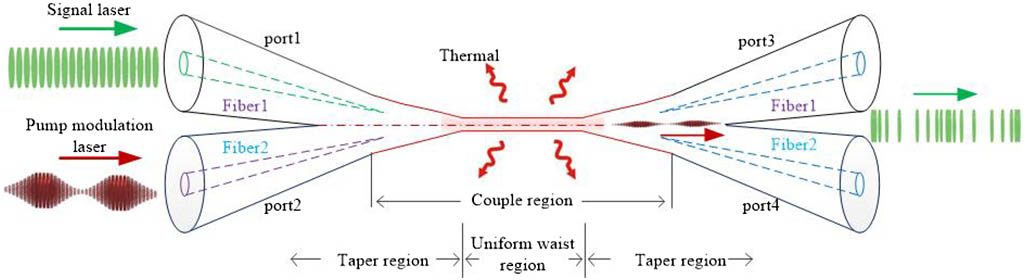
An all-optical intensity modulator based on an optical microfiber coupler (OMC) is presented. The modulator works at 1550 nm wavelength and is modulated directly by heating the coupling region with 980 nm pump light injected through the coupling port of the OMC. The OMC is controlled to have at least a 30 mm long coupling region with diameter smaller than 8 μm, and the uniform waist region diameter is about 3 μm. This is helpful to ensure the optical modulation function based on the light induced thermal effect in the coupling region, while pump light is injected. The modulation response is measured to show good linearity when the 980 nm pump light has a lower intensity (with power below 2.5 mW), which proves that the OMC acts as an all-optical modulator. The bandwidth of the modulator can be at 0.2–50 kHz with the average power of the intensity-modulated pump light about 2 mW, which can be further improved by optimizing the design of the coupler. The demonstrated modulator may have potential value for the application in an all-optical integration system.
230.4000 Microstructure fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 040605
1 国防科技大学文理学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学海洋科学与工程研究院, 湖南 长沙 410073
对微纳光纤耦合器(OMC)光吸收致热引起的全光强度调控特性进行了理论分析和实验研究。理论分析结果显示,OMC全光强度调控器件的调制响应效率与OMC腰区长度、抽运光在OMC腰区的损耗系数及抽运调制光强成正比,而与OMC腰区耦合光纤的半径成反比。通过实验将强度调制的980 nm抽运光注入OMC以加热其腰区,实现了对OMC传输的1550 nm工作光的全光调控功能。在百微瓦量级的调控光功率作用下,OMC全光强度调控器件即可实现整周期、大调制深度的强度调制,且在较小调制光功率下,调制响应信号幅度与调制信号幅度呈线性响应关系。OMC光热调控最小响应调制光功率为几十微瓦量级。研究成果为开发基于OMC光致热效应的光衰减、光开关及强度调制器等全光功能器件提供了实验数据,并为微纳光子集成光路热稳定性管控及片基量子通信系统安全性研究提供了可借鉴的研究方案。
光纤光学 微纳光纤耦合器 全光调制 光致热效应 光热效应 强度调制

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Academy of Ocean Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Optoelectronics Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
We propose a compensation technique based on pulse reference for intensity-modulated optical fiber sensors that can compensate the power fluctuation of the light source, the change of optical components transmission loss, and the coupler splitting ratio. The theoretical principle of this compensation technique is analyzed and a temperature sensor based on fiber coating-covered optical microfiber is carried out to demonstrate the compensation effect. The system noise is measured to be 0.0005 dB with the temperature sensitivity reaching 0.063 dB/°C, and the output drift is 0.006 dB in 2 h at room temperature. The output shows a slight variation (0.0061 dB) when the light source and the common light path suffer a 3 dB attenuation fluctuation.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(12): 120603
1 中国科学院 光电研究院,北京 100094
2 中国科学院 研究生院,北京 100080
为满足天文导航设备星敏感器内场高精度检测和标校的实际工程需要,设计了一种结构简单并且具有光反馈功能的新型高精度单星模拟器。选用发光二极管作为光源,采用先聚焦再准直的方法实现模拟星光的平行输出。星模拟器的光反馈系统可以在输出光强发生变化的时候自动调节星光光源的发光强度,从而使星模拟器的输出光强在相当长的时间段内保持稳定。星模拟器输出光束的平行度达到8″,输出光束的均匀性达到80 %,在连续工作至少8 h的情况下输出光束的稳定性达到89 %。相对稳定的输出光强减少了星模拟器因为模拟的星等发生变化而产生的影响,提高了星敏感器检测和标定的精度。
星模拟器 光反馈 光学系统设计 star simulator optical feedback optical system design
1 中国科学院光电研究院光电工程部, 北京 100094
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100049
共焦显微术是一种重要的微小物体成像技术,由于具有高精度、高分辨率及容易实现三维重构图像的优势而被广泛应用于微纳三维形貌测量。近年来,并行共焦显微检测技术引起各国专家的广泛关注,该技术将单点扫描变为多路同时并行探测,大大提高了三维检测速度。综述了并行共焦显微检测技术的基本原理,系统论述了近年来国内外在并行共焦显微检测技术方面的研究进展以及作者在这方面的研究。按照实现并行检测的方法对7种并行共焦显微检测技术进行了分类介绍,并指出了各种方法的优缺点。最后总结了目前存在的技术难题,分析了未来的发展趋势,为我国进一步开展此项研究提供技术参考。
显微术 并行共焦显微术 微纳检测 数字微镜 静态扫描 激光与光电子学进展
2012, 49(8): 080006





